Learn more about Google Tag Manager, the tag management system for businesses to measure the success of your online advertising. Without complicated codes, you benefit from an efficient solution to embed and manage tracking codes. With Google Tag Manager, you can analyse user behaviour on your website and make changes flexibly, without any technical support. In addition, learn with a step-by-step guide how you can easily optimise the success measurement of your marketing activities with the help of the Google Tag Manager, from installing the Google Tag Manager to setting up the tags.
Introduction to the Google Tag Manager
Google Tag Manager is a tag management system that helps companies measure the impact of their advertising on the web. With the help of the Google Tag Manager, tracking codes, also known as tags, can be embedded in the source code of a website to analyse the behaviour of users on the website. Compared to the traditional method, which requires programming knowledge, the Google Tag Manager offers an efficient solution to implement and manage tracking codes. An important advantage of Google Tag Manager is that companies are independent of programmers or developers to add or change tracking codes. This allows marketing teams to make changes flexibly and quickly without having to rely on technical support. The centralised management of tags enables efficient coordination and implementation of different marketing tags, such as for website analytics, conversion tracking, event tracking and custom tags.
Funktionsweise des Google Tag Managers
Containers
The Google Tag Manager works with containers. A container is a central platform where all tracking codes and tags for website analytics, event tracking, conversion tracking and other marketing tags are managed. There can be multiple containers in an account, each with its own container ID. If you have multiple websites under management, it is recommended to create a separate container for each site. The tags, triggers and variables are located within the container.
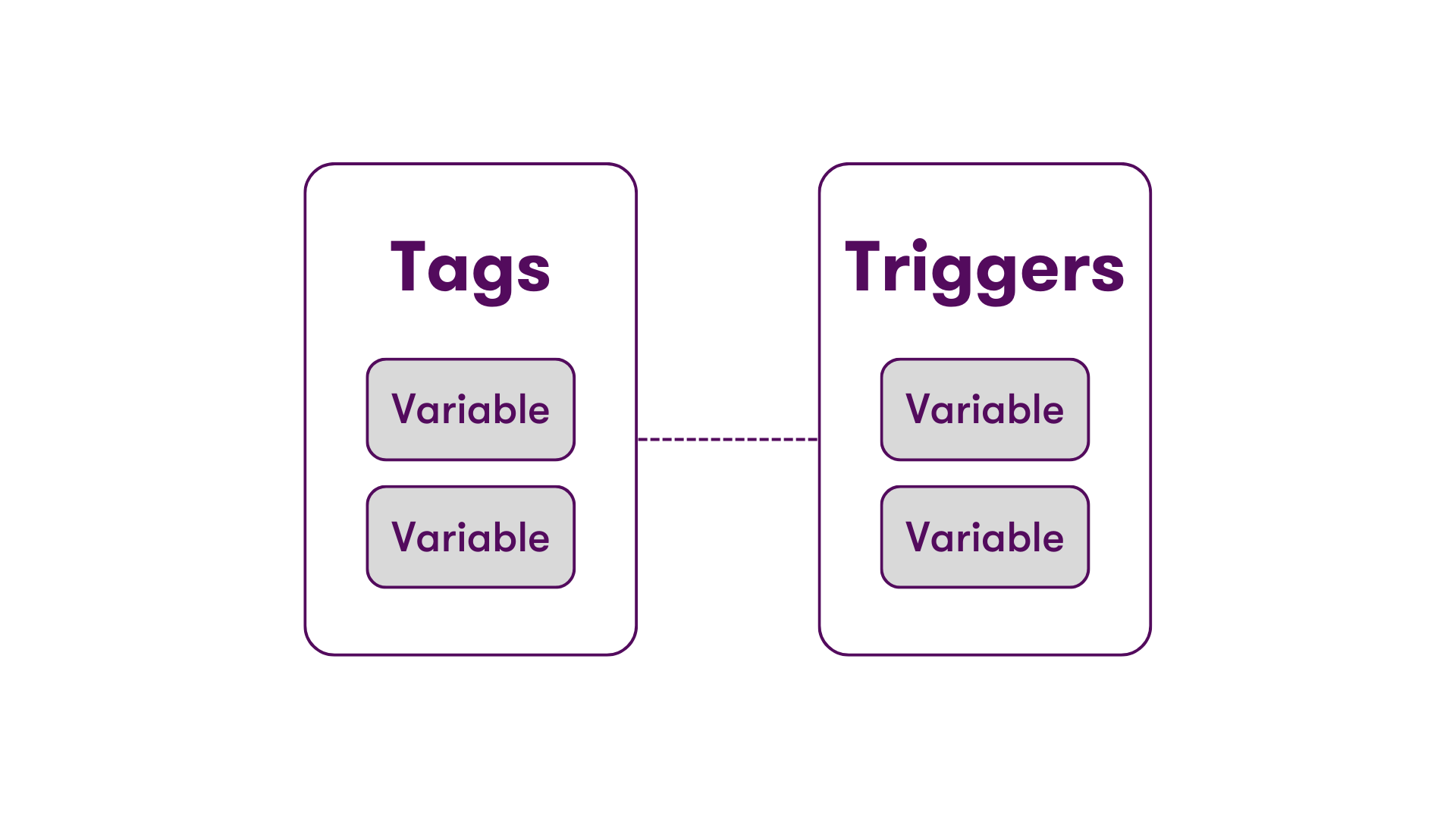
Tags
A tag is a snippet of code that runs on a web page or in a mobile app. Tags have different uses, but most tags are used to send measurement information from your website to a third-party provider. Examples include the Google Analytics tag and the Google Ads conversion tag. These tags are executed in response to events. Events can be page views, button clicks, scrolling, etc. In Google Tag Manager, you define triggers to listen for these events and determine when tags should be executed.
Triggers
In Google Tag Manager, a trigger monitors your website or mobile app for specific types of events such as form submissions, button clicks or page views. The trigger activates a tag when the specified event is detected.
Variables
Variables transmit the correct value to the tag and give the trigger the signal to activate. The variables only must be defined once. There are user-defined variables and integrated variables. Integrated variables are predefined because they are present on most web pages. An example of this could be the variable "clicks" if the clicks on the web page want to be tracked. User-defined variables can be entered by the user as needed.
Management of tags and tracking codes
The management of tags and tracking codes is very efficient in Google Tag Manager, which is crucial for the functioning of the tag management system. Companies can use Google Tag Manager to centrally manage and implement diverse types of tags, such as tracking codes for website analytics, marketing tags for conversion tracking or custom tags. Through effective data management and event tracking, Google Tag Manager enables precise data tracking and analytics integration.
Illustrative example
-
Tag: What should the Google Tag Manager do? Measure a Google Ads Conversion Tag
-
Trigger: When should this be measured? Under what circumstances? For a "thank you for buying" page
-
Variable: What/when/how exactly will be measured? If the page URL contains /purchase-successful/.

Application possibilities of the Google Tag Manager
Website analysis with Google Analytics
Google Tag Manager offers a wide range of uses, including comprehensive website analysis with Google Analytics. By integrating Google Tag Manager with Google Analytics, companies can gain detailed insights into the behaviour of visitors to their website. They can set up various tracking codes and tags to capture clicks, page views, conversions and other important metrics. In addition, Google Tag Manager allows you to seamlessly integrate other analytics tools and custom tags to optimise specific aspects of website analytics. By combining Google Tag Manager with Google Analytics, businesses gain valuable information to optimise their online presence, increase conversion rates and make informed decisions about their marketing strategies.
Conversion tracking for advertising campaigns
Google Tag Manager can also be used in conversion tracking for advertising campaigns. By integrating the Google Tag Manager with various advertising platforms, companies can collect detailed information about the success of their online advertising campaigns. The Tag Manager enables the easy implementation of conversion tracking tags to record and track conversions, such as purchases, sign-ups, or downloads. This gives companies important insights into the behaviour of users after they have clicked on an ad. This way, advertising strategies can be optimised accordingly.
Event tracking and user interactions
Event tracking and user interactions provide companies with valuable insights into the behaviour of their website visitors. By implementing appropriate tags, companies can analyse user behaviour, such as clicks on certain elements, interactions with forms or the completion of transactions. This detailed information allows companies to better understand user behaviour and make targeted optimisations to improve website usability, conversion rates and the overall user experience.
Third-party tag integration
Another important use of Google Tag Manager is the seamless integration of third-party tags. Companies can use Tag Manager to easily integrate tracking codes and scripts from other tools and vendors into their website without having to manually edit the source code. This makes it much easier to implement third-party marketing tags, such as for social media pixels, remarketing or ads. The central management of these tags enables efficient coordination and updating, so that companies can react flexibly to changes and adapt their marketing strategies.
Best practices for the use of Google Tag Manager
Structuring the tag management
When using the Google Tag Manager, it is important to establish a structured and well-organised approach. Careful planning and categorisation of tags enables efficient management and simplifies future changes or extensions. For example, it is advisable to group tags according to their function or purpose and to use custom variables and macros to optimise the configuration. Furthermore, it is advisable to set up clear version control to be able to track changes and undo them if necessary.
Versioning and testing of changes
For effective use of Google Tag Manager, it is advisable to follow best practices, especially regarding versioning and testing changes. Careful versioning makes it possible to create and manage different versions of tags and their configurations. This allows for better tracking of changes and easy recovery of previous versions when needed. In addition, it is significant to thoroughly test changes before they are released to ensure that they work correctly and deliver the expected results. By testing changes in a safe environment, potential errors or unwanted effects can be avoided. A systematic approach to versioning and testing changes helps to ensure reliable and consistent tag implementation and minimises the risk of errors or data loss.
Troubleshooting and common problems
Debugging tools and diagnostic options
When using the Google Tag Manager, errors may occasionally occur that can affect the correct functioning of the tags and tracking codes. In such cases, it is important to have appropriate troubleshooting methods and diagnostic capabilities. Google Tag Manager provides various debugging tools and diagnostic functions that allow companies to identify and fix potential problems. These include, for example, the preview and debug console, with which the tags can be checked before publication and errors can be analysed. In addition, the Google Tag Manager offers detailed error logs and reporting functions to perform a comprehensive analysis of tracking errors and respond appropriately to correct errors.
Resolving common error messages
To identify and resolve any errors that affect the proper functionality of the implemented tags, it is important to understand the common error messages and find appropriate solutions. For example, there may be conflicts between different tags, incorrect configurations, or problems with data transmission. By using debugging tools and diagnostic options of the Google Tag Manager, errors can be quickly detected and corrected. It is advisable to check the source code of the website, reconsider trigger settings and make changes if necessary. Careful error analysis and correction ensures smooth functioning of the Google Tag Manager and enables reliable collection and evaluation of the required tracking data.
Conclusion and summary
The Google Tag Manager is a powerful tag management system that helps companies measure and optimise their advertising efforts on the web. With Google Tag Manager, tracking codes can be efficiently implemented and managed without the need for technical knowledge. This enables marketing teams to make changes flexibly and quickly and to coordinate different marketing tags centrally. Google Tag Manager offers a wide range of uses, including website analysis with Google Analytics, conversion tracking for advertising campaigns, event tracking and the integration of third-party tags. Overall, by centrally managing tags and tracking codes, Google Tag Manager enables precise data tracking and Analytics integration that helps businesses optimise their online presence and make informed decisions for their marketing strategies.